Almost all American Grains Are Contaminated with Glyphosate Herbicide
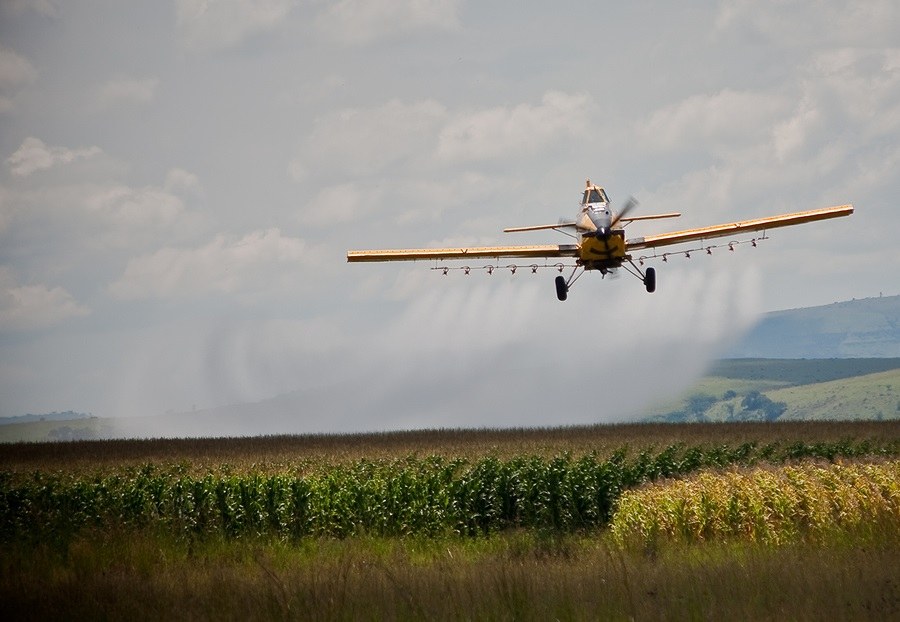
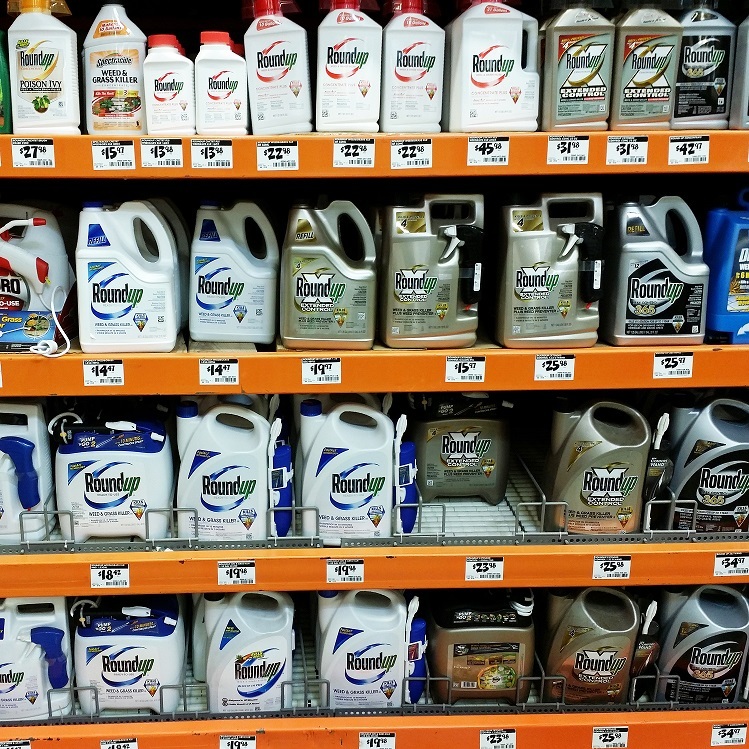
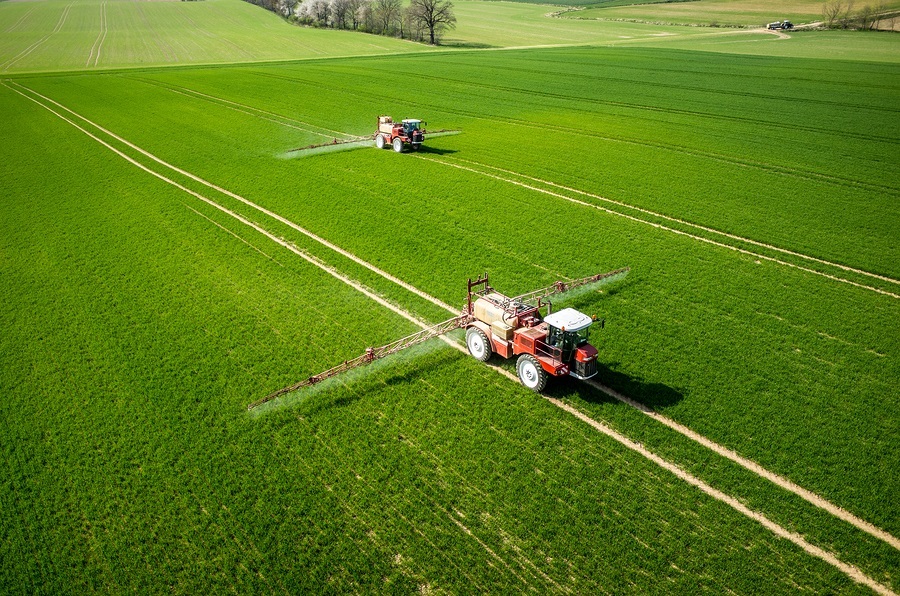
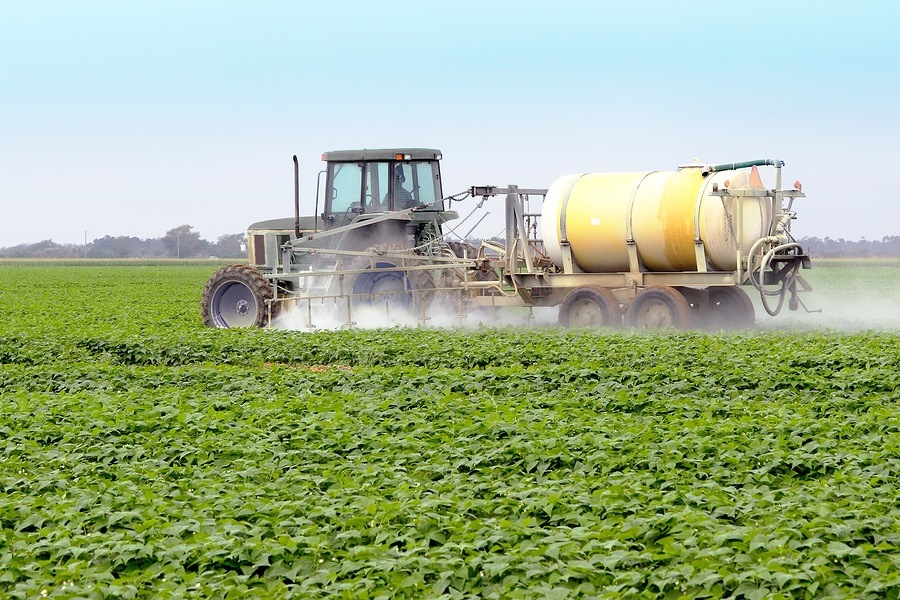
Glyphosate, the main ingredient in Monsanto’s Roundup herbicide, is recognized as the world’s most widely used weed killer. What is not so well known is that farmers also use glyphosate on crops such as wheat, oats, edible beans and other crops right before harvest, raising concerns that the herbicide could get into food products. According to Tom Ehrhardt, co-owner of Minnesota-based Albert Lea Seeds, sourcing grains not desiccated with glyphosate prior to harvest is a challenge. “I have talked with millers of conventionally produced grain and they all agree it’s very difficult to source oats, wheat, flax and triticale, which have not been sprayed with glyphosate prior to harvest,” he said. “It’s a ‘don’t ask, don’t tell policy’ in the industry.” “Can you imagine the public’s response if they knew that glyphosate is being sprayed on the oats in their Cheerios only weeks before it is manufactured?” Ehrhardt asked.