Antibiotic Catastrophe Being Hid from the Public
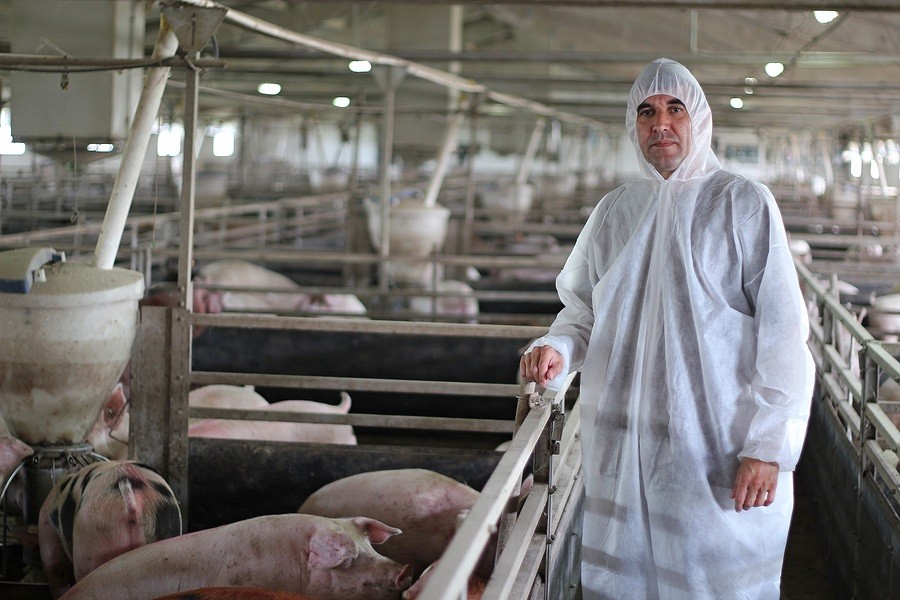
Antibiotic-resistant disease is a major health threat around the globe, such that illnesses once easily treatable with the drugs are now becoming deadly. The cause of the antibiotic-resistance epidemic is quite straightforward: overuse of antibiotics. “Resistant bacteria are more common in settings where antibiotics are frequently used: health care settings, the community and food animal production,” the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states — and the latter category is of utmost importance. The majority of antibiotics in the U.S. aren’t used in health care settings for humans; they’re used in industrial agriculture, primarily in low, steady doses for purposes of “disease prevention” (which also has the “side effect” of growth promotion, making the animals get bigger, faster). Despite this, exactly how and in what numbers antibiotics are used on U.S farms is a mystery, in large part because, as Wired put it, the data “isn’t considered an obligation owed to public health … it’s a political football.”