How to Prevent the Spread of Drug-Resistant Bacteria in Your Kitchen
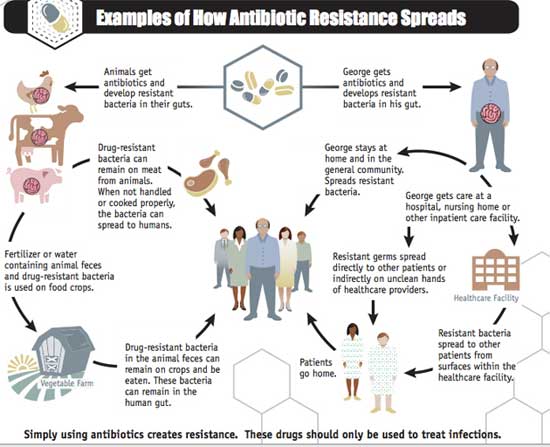
Two million American adults and children become infected with antibiotic-resistant bacteria each year. At least 23,000 of them die as a direct result of those infections. According to the CDC, as many as 22 percent of antibiotic-resistant illness in humans is linked to food, and research has shown that nearly half of all meats sold in the US harbor drug-resistant bacteria. These drug-resistant bacteria can easily spread during food preparation in your own kitchen. Learn how to avoid cross-contamination with other foods and the spread of potentially harmful bacteria in your kitchen.