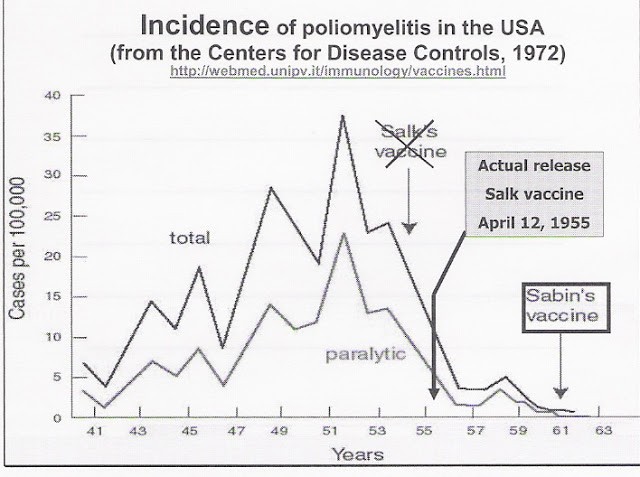
For the last 33 years, David Healy, an Irish psychiatrist and professor at Cardiff University School of Medicine in Wales, has written heavily researched university press books and academic journal articles on various aspects of psychopharmaceuticals. His output includes 20 books, 150 peer-reviewed papers and 200 other published works. He is not only well-pedigreed, with degrees and fellowships from Dublin, Galway and Cambridge medical schools, he is a widely recognized expert in both the history and the science of neurochemistry and psychopharmacology.
Yet Healy says his output and reputation have had little to no effect—both on the pharmaceutical industry he argues buries relevant information about prescription drug harms, and on the psychiatric and medical professions he claims are being “eclipsed” by drug companies.
Americans consume 80 percent of opiate painkillers produced in the world. A January 2011 report from Stanford University Medical School warned that antispychotics are now regularly being prescribed to treat conditions for which they have not been approved, including anxiety, attention-deficit disorder, sleep difficulties, behavioral problems in toddlers and dementia.
According to a Feb. 7, 2013 report from Drugs.com, the No. 1 best-selling U.S. drug (in dollar volume) is an atypical antipsychotic for schizophrenia treatment called Abilify. Sales for the last quarter of 2012 soared to $1.5 billion, because Abilify is widely prescribed off-label—i.e., not for schizophrenia in adults, but, for example, for irritability in children. Although Bristol-Myers Squibb, the maker of Abilify, was fined $515 million in September 2007 for recommending off-label uses of Abilify, doctors are still doling out the drug. Why?